Data Fusion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Data fusion is the process of integrating multiple data sources to produce more consistent, accurate, and useful information than that provided by any individual data source.
Data fusion processes are often categorized as low, intermediate, or high, depending on the processing stage at which fusion takes place. Low-level data fusion combines several sources of raw data to produce new raw data. The expectation is that fused data is more informative and synthetic than the original inputs.
For example,
Data fusion is the process of integrating multiple data sources to produce more consistent, accurate, and useful information than that provided by any individual data source.
Data fusion processes are often categorized as low, intermediate, or high, depending on the processing stage at which fusion takes place. Low-level data fusion combines several sources of raw data to produce new raw data. The expectation is that fused data is more informative and synthetic than the original inputs.
For example,
 In the mid-1980s, the Joint Directors of Laboratories formed the Data Fusion Subpanel (which later became known as the Data Fusion Group). With the advent of the World Wide Web, data fusion thus included data, sensor, and information fusion. The JDL/DFIG introduced a model of data fusion that divided the various processes. Currently, the six levels with the Data Fusion Information Group (DFIG) model are:
Level 0: ''Source Preprocessing'' (or ''Data Assessment'')
Level 1: ''Object Assessment''
Level 2: ''Situation Assessment''
Level 3: ''Impact Assessment'' (or ''Threat Refinement'')
Level 4: ''Process Refinement'' (or ''Resource Management'')
Level 5: ''User Refinement'' (or ''Cognitive Refinement'')
Level 6: ''Mission Refinement'' (or ''Mission Management'')
Although the JDL Model (Level 1–4) is still in use today, it is often criticized for its implication that the levels necessarily happen in order and also for its lack of adequate representation of the potential for a human-in-the-loop. The DFIG model (Level 0–5) explored the implications of situation awareness, user refinement, and mission management. Despite these shortcomings, the JDL/DFIG models are useful for visualizing the data fusion process, facilitating discussion and common understanding, and important for systems-level information fusion design.
In the mid-1980s, the Joint Directors of Laboratories formed the Data Fusion Subpanel (which later became known as the Data Fusion Group). With the advent of the World Wide Web, data fusion thus included data, sensor, and information fusion. The JDL/DFIG introduced a model of data fusion that divided the various processes. Currently, the six levels with the Data Fusion Information Group (DFIG) model are:
Level 0: ''Source Preprocessing'' (or ''Data Assessment'')
Level 1: ''Object Assessment''
Level 2: ''Situation Assessment''
Level 3: ''Impact Assessment'' (or ''Threat Refinement'')
Level 4: ''Process Refinement'' (or ''Resource Management'')
Level 5: ''User Refinement'' (or ''Cognitive Refinement'')
Level 6: ''Mission Refinement'' (or ''Mission Management'')
Although the JDL Model (Level 1–4) is still in use today, it is often criticized for its implication that the levels necessarily happen in order and also for its lack of adequate representation of the potential for a human-in-the-loop. The DFIG model (Level 0–5) explored the implications of situation awareness, user refinement, and mission management. Despite these shortcomings, the JDL/DFIG models are useful for visualizing the data fusion process, facilitating discussion and common understanding, and important for systems-level information fusion design.
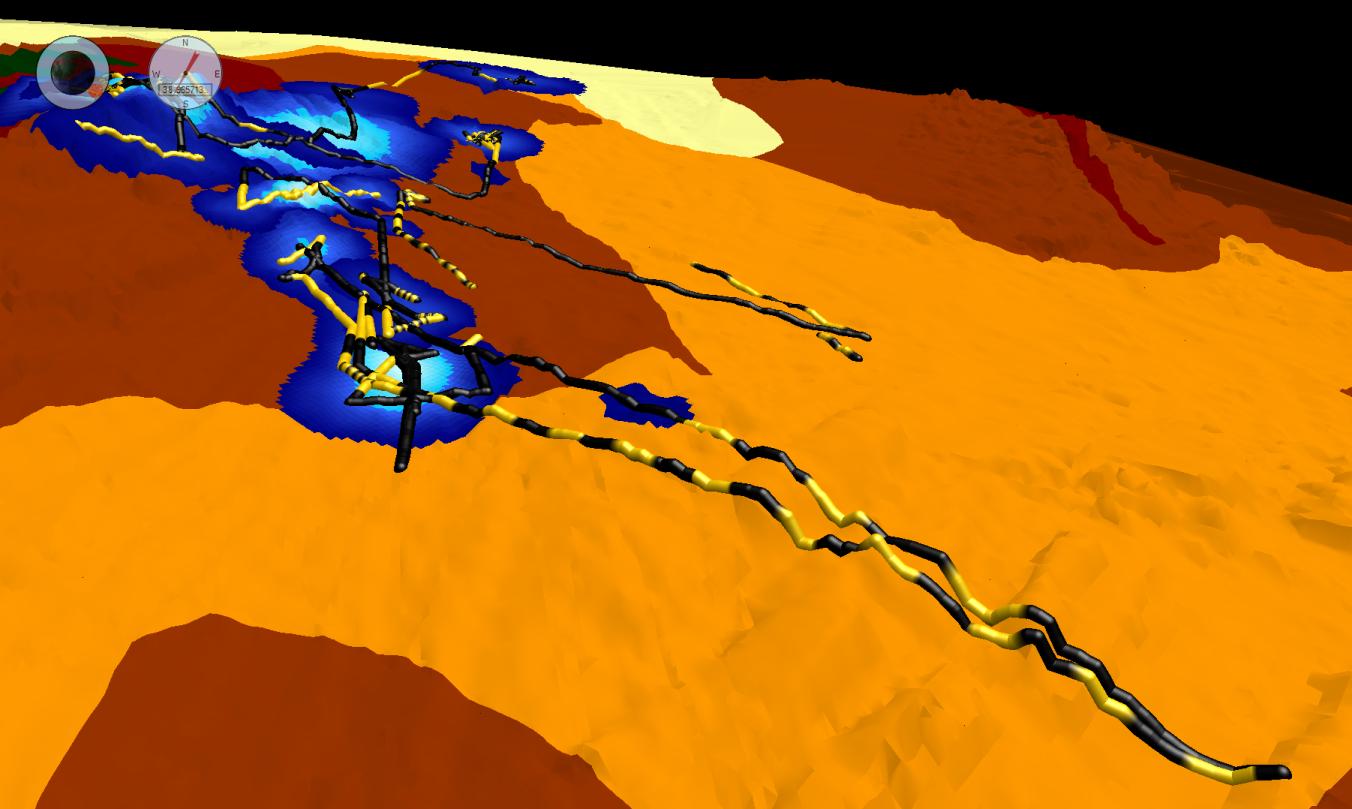 In a much more complicated application, marine animal researchers use data fusion to combine animal tracking data with
In a much more complicated application, marine animal researchers use data fusion to combine animal tracking data with
Discriminant Correlation Analysis (DCA)
International Society of Information Fusion
Sensor Fusion for Nanopositioning
{{DEFAULTSORT:Data Fusion Data analysis
 Data fusion is the process of integrating multiple data sources to produce more consistent, accurate, and useful information than that provided by any individual data source.
Data fusion processes are often categorized as low, intermediate, or high, depending on the processing stage at which fusion takes place. Low-level data fusion combines several sources of raw data to produce new raw data. The expectation is that fused data is more informative and synthetic than the original inputs.
For example,
Data fusion is the process of integrating multiple data sources to produce more consistent, accurate, and useful information than that provided by any individual data source.
Data fusion processes are often categorized as low, intermediate, or high, depending on the processing stage at which fusion takes place. Low-level data fusion combines several sources of raw data to produce new raw data. The expectation is that fused data is more informative and synthetic than the original inputs.
For example, sensor fusion
Sensor fusion is the process of combining sensor data or data derived from disparate sources such that the resulting information has less uncertainty than would be possible when these sources were used individually. For instance, one could potentia ...
is also known as (multi-sensor) data fusion and is a subset of information fusion
Information integration (II) is the merging of information from heterogeneous sources with differing conceptual, contextual and typographical representations. It is used in data mining and consolidation of data from unstructured or semi-structured ...
.
The concept of data fusion has origins in the evolved capacity of humans and animals to incorporate information from multiple senses to improve their ability to survive. For example, a combination of sight, touch, smell, and taste may indicate whether a substance is edible.
The JDL/DFIG model
 In the mid-1980s, the Joint Directors of Laboratories formed the Data Fusion Subpanel (which later became known as the Data Fusion Group). With the advent of the World Wide Web, data fusion thus included data, sensor, and information fusion. The JDL/DFIG introduced a model of data fusion that divided the various processes. Currently, the six levels with the Data Fusion Information Group (DFIG) model are:
Level 0: ''Source Preprocessing'' (or ''Data Assessment'')
Level 1: ''Object Assessment''
Level 2: ''Situation Assessment''
Level 3: ''Impact Assessment'' (or ''Threat Refinement'')
Level 4: ''Process Refinement'' (or ''Resource Management'')
Level 5: ''User Refinement'' (or ''Cognitive Refinement'')
Level 6: ''Mission Refinement'' (or ''Mission Management'')
Although the JDL Model (Level 1–4) is still in use today, it is often criticized for its implication that the levels necessarily happen in order and also for its lack of adequate representation of the potential for a human-in-the-loop. The DFIG model (Level 0–5) explored the implications of situation awareness, user refinement, and mission management. Despite these shortcomings, the JDL/DFIG models are useful for visualizing the data fusion process, facilitating discussion and common understanding, and important for systems-level information fusion design.
In the mid-1980s, the Joint Directors of Laboratories formed the Data Fusion Subpanel (which later became known as the Data Fusion Group). With the advent of the World Wide Web, data fusion thus included data, sensor, and information fusion. The JDL/DFIG introduced a model of data fusion that divided the various processes. Currently, the six levels with the Data Fusion Information Group (DFIG) model are:
Level 0: ''Source Preprocessing'' (or ''Data Assessment'')
Level 1: ''Object Assessment''
Level 2: ''Situation Assessment''
Level 3: ''Impact Assessment'' (or ''Threat Refinement'')
Level 4: ''Process Refinement'' (or ''Resource Management'')
Level 5: ''User Refinement'' (or ''Cognitive Refinement'')
Level 6: ''Mission Refinement'' (or ''Mission Management'')
Although the JDL Model (Level 1–4) is still in use today, it is often criticized for its implication that the levels necessarily happen in order and also for its lack of adequate representation of the potential for a human-in-the-loop. The DFIG model (Level 0–5) explored the implications of situation awareness, user refinement, and mission management. Despite these shortcomings, the JDL/DFIG models are useful for visualizing the data fusion process, facilitating discussion and common understanding, and important for systems-level information fusion design.
Geospatial applications
In the geospatial ( GIS) domain, data fusion is often synonymous withdata integration
Data integration involves combining data residing in different sources and providing users with a unified view of them.
This process becomes significant in a variety of situations, which include both commercial (such as when two similar companies ...
. In these applications, there is often a need to combine diverse data sets into a unified (fused) data set which includes all of the data points and time steps from the input data sets. The fused data set is different from a simple combined superset in that the points in the fused data set contain attributes and metadata which might not have been included for these points in the original data set.
A simplified example of this process is shown below where data set "α" is fused with data set β to form the fused data set δ. Data points in set "α" have spatial coordinates X and Y and attributes A1 and A2. Data points in set β have spatial coordinates X and Y and attributes B1 and B2. The fused data set contains all points and attributes.
In a simple case where all attributes are uniform across the entire analysis domain, the attributes may be simply assigned: ''M?, N?, Q?, R?'' to M, N, Q, R. In a real application, attributes are not uniform and some type of interpolation is usually required to properly assign attributes to the data points in the fused set.
 In a much more complicated application, marine animal researchers use data fusion to combine animal tracking data with
In a much more complicated application, marine animal researchers use data fusion to combine animal tracking data with bathymetric
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors (''seabed topography''), lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water d ...
, meteorological, sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air mas ...
(SST) and animal habitat data to examine and understand habitat utilization and animal behavior in reaction to external forces such as weather or water temperature. Each of these data sets exhibit a different spatial grid and sampling rate so a simple combination would likely create erroneous assumptions and taint the results of the analysis. But through the use of data fusion, all data and attributes are brought together into a single view in which a more complete picture of the environment is created. This enables scientists to identify key locations and times and form new insights into the interactions between the environment and animal behaviors.
In the figure at right, rock lobsters are studied off the coast of Tasmania. Hugh Pederson of the University of Tasmania
The University of Tasmania (UTAS) is a public research university, primarily located in Tasmania, Australia. Founded in 1890, it is Australia's fourth oldest university. Christ College, one of the university's residential colleges, first prop ...
used data fusion software to fuse southern rock lobster
''Jasus edwardsii'', the southern rock lobster, red rock lobster, or spiny rock lobster, is a species of spiny lobster found throughout coastal waters of southern Australia and New Zealand including the Chatham Islands. It is commonly called '' ...
tracking data (color-coded for in yellow and black for day and night, respectively) with bathymetry and habitat data to create a unique 4D picture of rock lobster behavior.
Data integration
In applications outside of the geospatial domain, differences in the usage of the termsData integration
Data integration involves combining data residing in different sources and providing users with a unified view of them.
This process becomes significant in a variety of situations, which include both commercial (such as when two similar companies ...
and Data fusion apply. In areas such as business intelligence, for example, data integration is used to describe the combining of data, whereas data fusion is integration followed by reduction or replacement. Data integration might be viewed as set combination wherein the larger set is retained, whereas fusion is a set reduction technique with improved confidence.
Application areas
* Bioinformatics *Biometrics
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify i ...
*Business intelligence
Business intelligence (BI) comprises the strategies and technologies used by enterprises for the data analysis and management of business information. Common functions of business intelligence technologies include reporting, online analytical p ...
*Business performance management
Business performance management (BPM), also known as corporate performance management (CPM) and enterprise performance management (EPM),) is a set of performance management and analytic processes that enables the management of an organization's p ...
* Cheminformatics
**Quantitative structure-activity relationship
Quantitative may refer to:
* Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties
* Quantitative analysis (disambiguation)
* Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry
* Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis ...
*Discovery science
Discovery science (also known as discovery-based science) is a scientific methodology which aims to find new patterns, correlations, and form hypotheses through the analysis of large-scale experimental data. The term “discovery science” enco ...
* Geospatial information systems
*Intelligence services
An intelligence agency is a government agency responsible for the collection, analysis, and exploitation of information in support of law enforcement, national security, military, public safety, and foreign policy objectives.
Means of informatio ...
* Intelligent transport systems
* Loyalty card
* Oceanography
*Soil mapping
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former term ...
*Wireless sensor networks
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) refer to networks of spatially dispersed and dedicated sensors that monitor and record the physical conditions of the environment and forward the collected data to a central location. WSNs can measure environmental c ...
From multiple traffic sensing modalities
The data from the different sensing technologies can be combined in intelligent ways to determine the traffic state accurately. A Data fusion based approach that utilizes the road side collected acoustic, image and sensor data has been shown to combine the advantages of the different individual methods.Decision fusion
In many cases, geographically dispersed sensors are severely energy- and bandwidth-limited. Therefore, the raw data concerning a certain phenomenon are often summarized in a few bits from each sensor. When inferring on a binary event (i.e., or ), in the extreme case only binary decisions are sent from sensors to a Decision Fusion Center (DFC) and combined in order to obtain improved classification performance.For enhanced contextual awareness
With a multitude of built-in sensors including motion sensor, environmental sensor, position sensor, a modern mobile device typically gives mobile applications access to a number of sensory data which could be leveraged to enhance the contextual awareness. Using signal processing and data fusion techniques such as feature generation, feasibility study and principal component analysis (PCA) such sensory data will greatly improve the positive rate of classifying the motion and contextual relevant status of the device. Many context-enhanced information techniques are provided by Snidaro, et al.Bayesian auto-regressive Gaussian processes
Gaussian processes are a popular machine learning model. If an auto-regressive relationship between the data is assumed, and each data source is assumed to be Gaussian process, this constitutes a non-linearBayesian regression
Bayesian linear regression is a type of conditional modeling in which the mean of one variable is described by a linear combination of other variables, with the goal of obtaining the posterior probability of the regression coefficients (as well ...
problem.
''See also Multifidelity Simulation''
See also
*Data assimilation
Data assimilation is a mathematical discipline that seeks to optimally combine theory (usually in the form of a numerical model) with observations. There may be a number of different goals sought – for example, to determine the optimal state es ...
*Data munging
Data wrangling, sometimes referred to as data munging, is the process of transforming and mapping data from one " raw" data form into another format with the intent of making it more appropriate and valuable for a variety of downstream purposes ...
*Image fusion
The image fusion process is defined as gathering all the important information from multiple images, and their inclusion into fewer images, usually a single one. This single image is more informative and accurate than any single source image, and i ...
*Information integration
Information integration (II) is the merging of information from heterogeneous sources with differing conceptual, contextual and typographical representations. It is used in data mining and consolidation of data from unstructured or semi-structured ...
*Integrative level An integrative level, or level of organization, is a set of phenomena emerging from pre-existing phenomena of a lower level. The levels concept is an intellectual framework for structuring reality. It arranges all entities, structures, and processes ...
*Meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting me ...
*Sensor fusion
Sensor fusion is the process of combining sensor data or data derived from disparate sources such that the resulting information has less uncertainty than would be possible when these sources were used individually. For instance, one could potentia ...
References
Sources
; General references * *Bibliography
* * *External links
Discriminant Correlation Analysis (DCA)
International Society of Information Fusion
Sensor Fusion for Nanopositioning
{{DEFAULTSORT:Data Fusion Data analysis